World warming is costing lives, deepening well being inequality and driving the unfold of disease-carrying ticks and parasites throughout Europe, in accordance with a serious report.
The report reviewed a whole lot of research on the well being results of local weather change — in addition to the actions being taken in response — in Europe. Local weather and well being researcher Rachel Lowe and her colleagues tracked 42 indicators, together with these on heat-related deaths, the unfold of infectious ailments and developments in analysis on well being and local weather change.
Excessive warmth harms well being — what’s the human physique’s restrict?
“We actually want some drastic motion to be taken by European nations to assist preserve the European inhabitants, and likewise populations throughout the globe, secure from the well being impacts of local weather change,” says Lowe, who’s on the Barcelona Supercomputing Middle and on the Catalan Establishment for Analysis and Superior Research in Spain.
The report, printed final month in Lancet Public Well being1, is the second — after one printed in 20222 — from a research referred to as ‘The Lancet Countdown: Well being and Local weather Change in Europe’.
“The report emphasizes the alarming improve in mortality and morbidity linked to rising temperatures, and the proliferation of climate-sensitive ailments,” says Ana Raquel Nunes, a well being and surroundings researcher on the College of Warwick, UK.
Researchers say that additional research ought to take a holistic method to the local weather–well being nexus. “You’ll be able to’t deal with all these well being impacts of local weather change in isolation,” says Ruth Doherty, a climate-change and well being researcher on the College of Edinburgh, UK. “We actually must learn about how these a number of exposures have an effect on the inhabitants.”
In three graphics, Nature outlines how a hotter world is affecting well being and analysis throughout Europe.
Lethal warmth
Lowe and her colleagues used mortality and temperature knowledge, in addition to prior proof for the way warmth influences mortality, to estimate that, from 2003–12 to 2013–22, heat-related mortality elevated by a median of 17 deaths per 100,000 individuals per 12 months throughout Europe. The rise in heat-related mortality was greater in ladies in contrast with males (See ‘Warmth kills’).
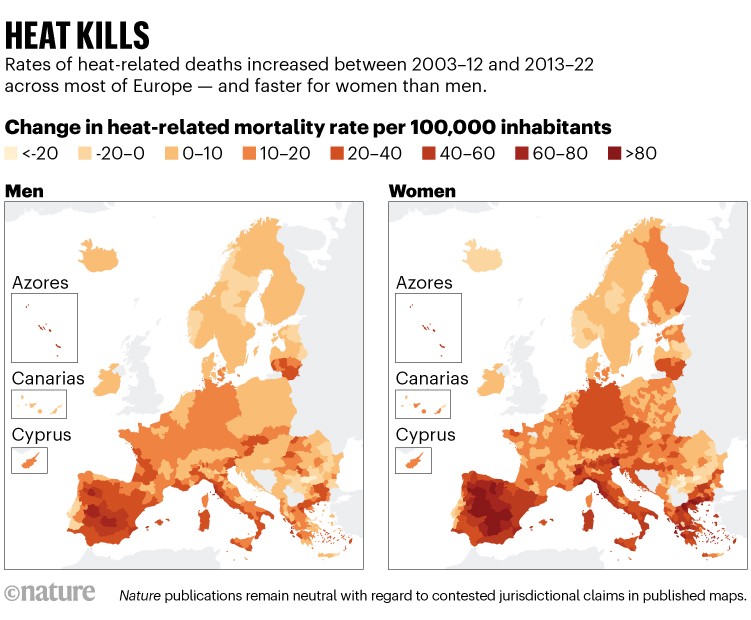
Supply: Ref 1.
“Gender disparities could also be defined by variations when it comes to dropping warmth from the physique and most sweat charges,” says Kim van Daalen, who research local weather change, illness and gender inequity on the Barcelona Supercomputing Middle. Girls may additionally usually be at better danger of warmth stress after ovulation, after they are inclined to have greater physique temperature, she says.
One other issue that could possibly be driving the gender hole is that ladies usually attain older ages than males, and older persons are usually extra susceptible to heat-related stresses, says Lowe. Older persons are additionally extra more likely to dwell alone, which places them in better hazard from warmth, she says.
Ticks and parasites
Hotter temperatures are enabling disease-carrying parasites to broaden into extra areas and spurring the expansion of tick populations. One pathogen that’s changing into extra widespread owing to local weather change is the single-cell parasite Leishmania infantum. It’s transmitted to individuals when feminine sandflies (Phlebotomus sp.) chunk human pores and skin to feed on blood. The parasite normally causes pores and skin ulcers throughout the physique, which could be debilitating. In excessive instances, it may well trigger fevers and the swelling of the spleen and liver, and could possibly be deadly.
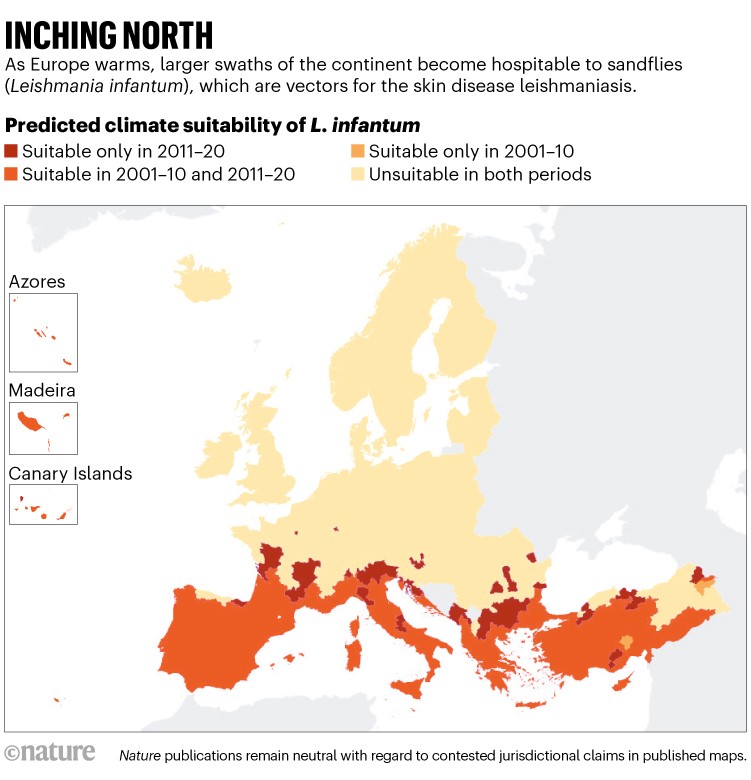
Supply: Ref 1.
The researchers estimated that hotter and more-humid situations throughout Europe have enabled sandflies and the parasites they carry to unfold north into new territories. Their vary was wider within the 2010s than within the 2000s. “Rising temperatures create extra beneficial situations for sandflies to outlive and reproduce,” says van Daalen. “Hotter situations may speed up the life cycle of the parasite inside sandflies,” she says (See ‘Inching North’).
The workforce additionally discovered that hotter temperatures have made Europe extra appropriate for the tick Ixodes ricinus, which might transmit a variety of ailments when it bites individuals. “Tick-borne ailments, corresponding to Lyme illness and tick-borne encephalitis, trigger signs starting from flu-like sickness to extreme neurological and cardiovascular issues, resulting in missed work, long-term incapacity and substantial health-care prices,” says van Daalen.
Throughout many of the continent, I. ricinus discovered a extra hospitable local weather to feed and develop in 2013–22 than it did in 1951–60, as measured by the common variety of months per 12 months when temperatures had been optimum for the juvenile stage of its life cycle.
Publishing increase
Because the world warms, analysis on how local weather change intersects with Europeans’ well being has intensified, as seen within the variety of papers tracked within the open-access database OpenAlex. The researchers counted a whole lot of research on how local weather change and Europeans’ well being intersect, printed between 1991 and 2022. The vast majority of these research targeted on how world warming impacts well being, however some additionally seemed into the greenhouse gases emitted by health-care methods, or the right way to shield individuals from local weather change that’s already occurring (See ‘Sizzling subject’).
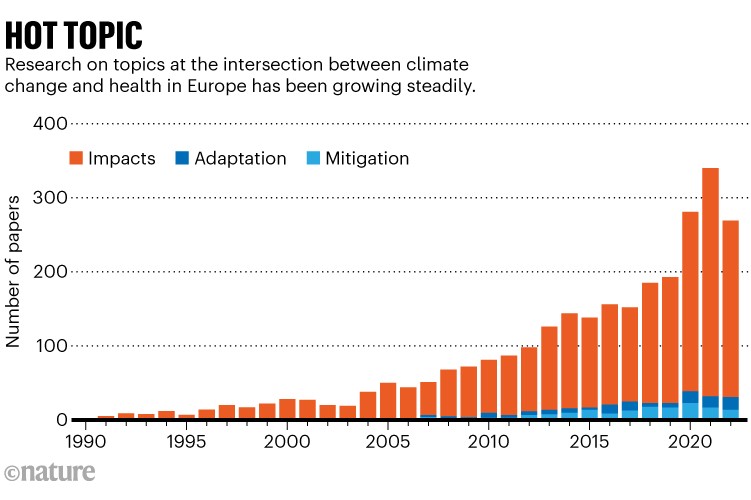
Ref 1.
The authors additionally discovered that round 2% of the research printed in 2022 on local weather well being referenced equality, fairness or justice. “This highlights a considerable hole in analysis,” says van Daalen. “To correctly reply to the climate-related well being impacts, you will need to perceive which populations are disproportionately affected and most in danger,” she says.



