
Researchers at Georgia Institute of Know-how within the US and Tianjin College in China collaborated to create the world’s first useful semiconductor constructed from graphene.Credit score: Georgia Inst. Technol.
China’s scientific collaboration with different nations has declined for the reason that pandemic, pushed by falling partnerships with the USA, an evaluation exhibits.
Scientists have been warning that political tensions between China and the USA, mixed with the pandemic, have affected analysis collaborations between the 2 nations. But it surely takes time for proof of this kind of decline to build up in analysis databases.
The most recent proof comes from an evaluation carried out by Springer Nature’s staff in China. (Nature’s information staff is editorially impartial of its writer, Springer Nature.) The authors used InCites, a device owned by publishing-analytics agency Clarivate, primarily based in London, to analyse internationally co-authored articles that had been printed between 2013 and 2023. InCites attracts on papers listed within the science-citation database Internet of Science.
They discovered that in 2022, the entire quantity papers co-authored by researchers from China and their worldwide friends declined for the primary time since 2013 (See ‘Analysis Powerhouse’).
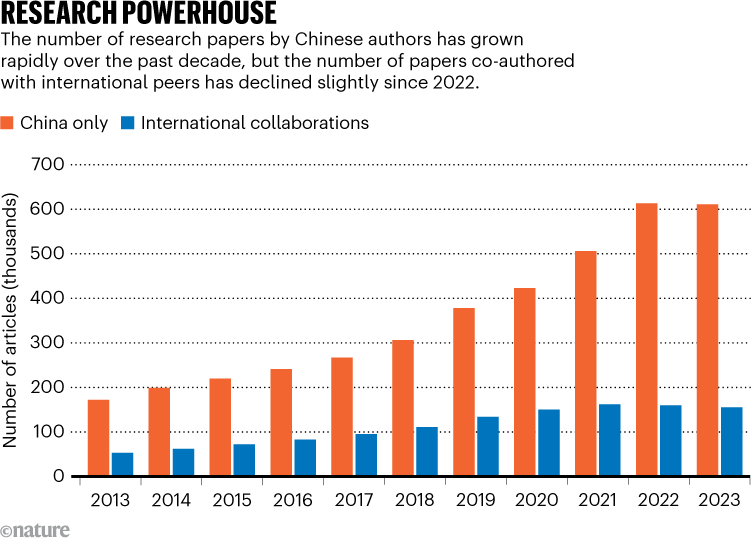
The proportion of analysis papers with Chinese language and worldwide co-authors has been falling for even longer. At its peak, in 2018, 26.6% — roughly 110,000 articles — of China’s output within the InCites database was co-authored with worldwide colleagues. By 2023, the proportion of the nation’s articles with worldwide friends had dropped by 7.2%, regardless of China’s total variety of articles virtually doubling to 759,000 over the identical interval.
The drop in internationally co-authored papers is principally as a consequence of China’s declining share of papers printed with US researchers, which fell by 6.4% between its peak in 2017 and 2023 — the most important decline of any nation included within the evaluation. The findings had been offered on the Zhongguancun Discussion board in Beijing on 25 April.
The decline in US-China collaborations echoes findings from a 2022 evaluation carried out for Nature, which discovered that the variety of researchers with twin US and China affiliations on analysis articles in Elsevier’s Scopus database had fallen by greater than 20% between 2019 and 2021.
Though the newest evaluation exhibits that the share of US–China articles has been slowly declining over the previous six years, the pandemic exacerbated the downward pattern, says Marina Zhang, an innovation researcher who focuses on China on the College of Know-how Sydney in Australia.
Political tensions
Zhang says that ongoing geopolitical tensions between the USA and China have additionally fuelled the decline. “That is particularly worrying for researchers,” says Zhang. The US Division of Justice’s controversial China Initiative — which was launched in 2018 to sort out espionage in analysis and business — resulted in 2022. The crackdown resulted in a number of scientists being arrested over their ties to collaborators or establishments in China, and has stoked worry amongst researchers of Chinese language descent. Since then, the US authorities has adopted a spread of insurance policies centered on tightening analysis safety. And in July 2023, the Chinese language authorities carried out its revised counter-espionage legislation, which broadened the definition of what constitutes spying.
The crackdown on perceived international interference in each the USA and China is making researchers extra cautious about collaborating, says Zhang. Restrictive insurance policies and the local weather of worry might find yourself driving expertise away from sure nations and fields, resulting in a “mind drain and a lack of invaluable human capital”, she says.
This “chilling impact” on US–China collaborations is already hindering influential analysis, says Tang Li, a researcher who focuses on science and innovation coverage at Fudan College in Shanghai, China. For example, a 2024 research examined the impact that the foreign-interference investigations on the US Nationwide Institutes of Well being (NIH) had on researchers and located that these in the USA with collaborators in China had been much less productive throughout this era than had been their colleagues with scientific companions in different nations1.
Zhang says that the faltering collaborative ties between the USA and China might additionally outcome within the nations pursuing the identical kinds of analysis individually, as an alternative of becoming a member of forces to sort out world issues similar to local weather change, pandemics and meals safety.
Turning inwards
Extra worryingly, the nations would possibly more and more prioritize home pursuits over worldwide cooperation, which might make scientific analysis a extra nationalistic endeavour, says Zhang.
China’s collaborations with different nations have additionally tapered off since 2020, however not as markedly as these with the USA. Tang says that reviving US–China collaborations is essential as a result of such scientific partnerships might assist to bridge the hole between the 2 nations. “Given the rising world disasters and uncertainties, humanity can not afford to waste time on nationalistic rivalries,” she says.


