
Trince’s LumiPore gadget permits a mixture of cells, and the molecules to go inside them, to be focused with a laser.Credit score: www.fuxfotografie.be
Kevin Braeckmans has all the time been fascinated by gentle. “I began finding out physics with the aim of turning into an experimental astronomer and utilizing superior telescopes to discover the universe,” he says. But, whereas engaged on his PhD, he discovered himself peering by microscopes as a substitute, at “one other a part of the universe that was in any other case inaccessible”, says Braeckmans, who now leads the Bio-Photonic Analysis Group at Ghent College in Belgium.
His PhD analysis targeted on nanomaterials for drug supply — an endeavour that made Braeckmans notice that the approaches scientists have been utilizing to get molecules inside cells was damaging the cells. Maybe, he thought, gentle would possibly present a gentler approach of carrying out this.
It was an concept that, in 2021, would result in the creation of Trince — a spin-off firm from Ghent College whose title is a portmanteau of ‘switch into cells’.
Braeckmans, along with co-founders Philip Mathuis and Stefaan De Smedt, developed a tool that makes use of a method referred to as photoporation to make non permanent holes within the cell membrane by which molecules could make their approach inside. The corporate’s mission is straightforward: to ship virtually something into virtually any kind of cell, within the gentlest approach attainable.
Now, the potential of that has been acknowledged by the judges of Nature’s Spinoff Prize, who chosen Trince as essentially the most promising of all of the competing firms. “They’ve constructed an incredible workforce, they’re open to mentorship, they usually have the precise technique,” says choose Kiana Aran, who research medical diagnostics and therapeutics on the Keck Graduate Institute in Claremont, California. “There may be far more potential to the expertise than they even have thought of,” she provides.
Fast warmth
Getting a molecule inside a cell, whether or not for analysis or therapeutic functions, is troublesome to do with out disrupting the cells. The big genetic constructs which are required in most cancers immunotherapy and regenerative drugs pose a specific problem.
The usual method to introduce genetic materials has been with viral vectors. However that course of is laborious and costly. Furthermore, the vectors may cause all types of hassle. They could, for instance, disrupt the cell’s personal genome by inserting the fabric in awkward locations, or go away markers on the cell that activate the immune system. The viruses might even regain their capability to breed, regardless of the method having been artificially disabled.
One vector-free strategy that has emerged is electroporation, which makes use of an electrical present to briefly disrupt the cell membrane. This avoids the downsides of viral vectors, however it typically kills lots of the cells it targets. “Corporations have a tendency to not promote what number of cells survive the electroporation, however relatively report on the viability of the remaining cells,” says Braeckmans.
Even among the many cells that survive, there’s a distinction between being technically alive and with the ability to proliferate and carry out the features required, Braeckmans factors out. As a result of {the electrical} fields utilized in electroporation penetrate the cells and trigger injury, the cells can take a number of days to recuperate sufficient to start out proliferating once more, in the event that they ever do, he says. “We are able to do higher than that.”
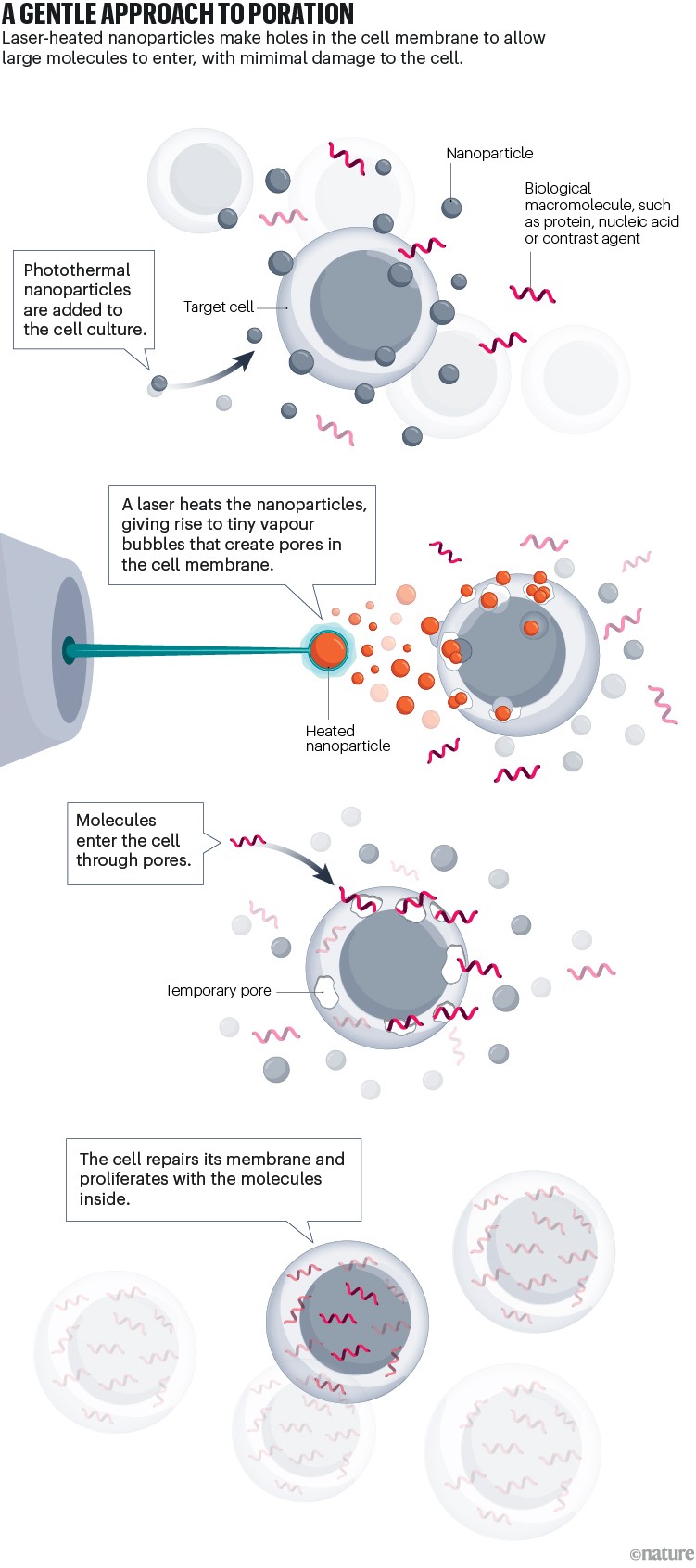
Much like electroporation, photoporation makes an attempt to ship molecules into the cell by creating tiny pores that make the cell membrane briefly permeable. In photoporation, nevertheless, vitality is absorbed not by the cell constructions, however by nanoparticles added to the cell-culture medium that surrounds the cell. These are designed to warmth up rapidly when illuminated by extraordinarily temporary (lower than 10 nanoseconds) bursts of pink laser gentle. The impact is analogous, Braeckmans says, to “how grains of sand in summer season choose up daylight and grow to be scorching”.
Relying on the quantity of vitality equipped by the laser, two processes can occur — each of them helpful. “At decrease ranges,” says Braeckmans, “the warmth creates non permanent burn wounds within the cell membrane by which the encompassing liquid will get in.” At increased ranges, the water across the particles boils, giving rise to rapidly increasing bubbles that may mechanically create pores within the cell membrane.
The bubbles, which will be seen below the microscope, final only some tens of nanoseconds (see ‘A delicate strategy to poration’). However the pores they create exist for tens of seconds, which Braeckmans says “is enough time for the molecules to get inside”. As with electroporation, a number of the cell’s contents would possibly leak out, however photoporation doesn’t in any other case injury the within of the cell. In consequence, extra cells survive the photoporation course of than make it by electroporation1.
Infographic by Alisdair Macdonald
Trince has now built-in this technique into LumiPore, a tool by which a cell-culture vessel, containing a mixture of cells, nanoparticles and the molecules to go contained in the cell, will be focused with laser gentle.
“The LumiPore expertise provides a safer and extra versatile ‘transfection’ technique in comparison with current options that largely work just for cell suspension, and it’s backed by robust preliminary research,” says engineer Hyunwoo Yuk, one of many judges for The Spinoff Prize 2024 and co-founder of SanaHeal, which gained The Spinoff Prize in 2023. He provides, nevertheless, that the sector of high-throughput cell expertise to introduce molecules into cells is crowded. “Many firms and start-ups have developed and commercialized competing options.”
To date, two LumiPore units appropriate for analysis have been offered. One among these was acquired by Revatis, an organization based mostly in Aye, Belgium, that produces stem cells to be used in cell remedy and regenerative drugs. “We’re utilizing it for the photoporation of a number of molecules and genetic materials into muscle-derived stem cells,” says chief government Didier Serteyn. “It’s a delicate expertise with a excessive proportion of dwelling cells after incorporation.”
Trince hopes to promote a minimum of seven extra units by the top of this 12 months. “We’re in contact with just a few high-ranked tutorial institutes to debate the potential of putting an instrument there that they’ll use to validate and conduct analysis with, and that they’ll use kind of at no cost for a restricted period of time,” says Jan Van Hauwermeiren, Trince’s vice-president for enterprise improvement. The aim, he says, is to acquire knowledge “to assist persuade different scientists”.
“Trince has been very clear about once they would grow to be worthwhile, what they wanted to get there and what they wanted it for,” says Sue Sundstrom, founding father of Sundstrom Innovation in Clevedon, UK, who chaired the Spinoff Prize judging committee.
Braeckmans hopes that the €30,000 ($32,000) prize will assist to kick off the corporate’s first vital spherical of enterprise capital financing. “This implausible recognition will assist us to get some publicity, and to get additional credibility for our firm, for our expertise, to safe new investments into the corporate,” he says.
Into the clinic
Final March, Trince acquired a grant from the European Innovation Council that ought to assist the corporate to develop the expertise for therapeutic functions, corresponding to most cancers immunotherapy and regenerative drugs, says Mathuis, the corporate’s chief government. “We are actually working to adjust to the US Meals and Drug Administration’s Present Good Manufacturing Follow laws for medical units,” he says.
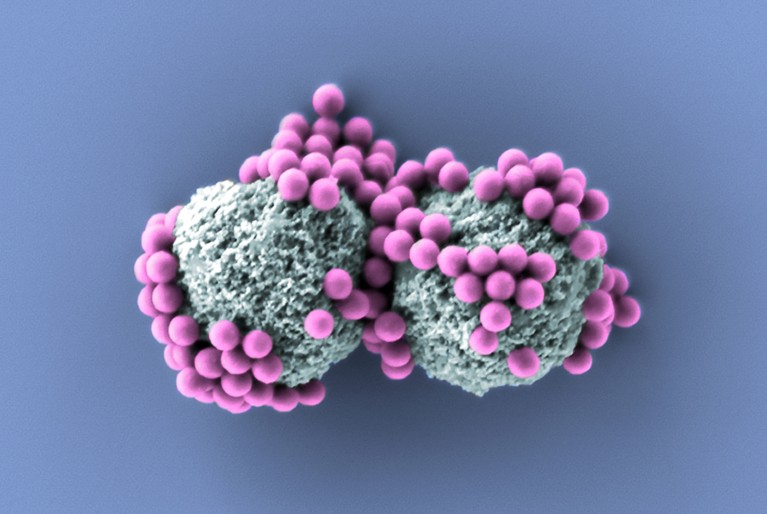
‘Nanobombs’ may very well be a very environment friendly type of photoporation.Credit score: Tailored from (ref to https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-022-29713-7)
One necessary side to work out might be how one can guarantee that the cells being ready for therapeutic use don’t comprise any of the dangerous nanoparticles that have been a part of the photoporation course of. In 2021, Braeckmans and his colleagues demonstrated1 that such particles will be embedded in nanofibres to maintain them from moving into the cell. “We think about that these fibre-embedded particles would be the central platform we are going to supply for cell-therapy functions, as a result of it’s safer to make use of,” says Braeckmans.
Nevertheless, free nanoparticles are sometimes simpler, he says, as a result of they’ll cowl your complete cell floor. With that in thoughts, Trince can be exploring biodegradable alternate options to the iron oxide-based nanoparticles that it at the moment makes use of. These would break down after some time even when they did get into the cell. “We’ve got a collection of nanoparticles which have all been patented for our functions, and we’re on the lookout for the precise stability between security and effectivity,” Braeckmans says. “We’re holding our choices open.”
The corporate can be working to make the photoporation of cells simpler and sooner. For instance, it’s creating a tool able to photoporating cells constantly and mechanically because the cells move by it. “This could permit for full automation, which ought to pace issues up and likewise assist to deliver the fee down,” says Mathuis.
Ultimately, the gadget would possibly assist hospitals to engineer cells themselves, making remedies sooner and extra reasonably priced. Folks with most cancers who’re awaiting T-cell therapy have completely no time to lose, says Braeckmans. “It’s typically within the last phases of therapy that these costly cell-based therapies are getting used. So lowering these ready instances can save lives.” T cells are significantly tough, he provides, as a result of they’re typically in a dormant state. This causes issues for applied sciences that require the cell to actively ingest particles — however not for photoporation.
Trince is constant to refine photoporation expertise. In 2022, Braeckmans and his colleagues reported a variation of the approach — referred to as biolistics or nanobombs — that guarantees to be even higher at holding cells alive2. This entails a central particle surrounded with smaller nanobullets that shoot off in all instructions when the core particle is heated with pulses of laser gentle. For delivering giant constructs into cells, this strategy will be a minimum of ten instances extra environment friendly than customary photoporation, says Braeckmans. As for what might be delivered with their instruments, Trince is leaving that to others. “We’re supply guys,” Braeckmans says. “We ship what different folks develop.”


